Translate this page into:
D-penicillamine-induced membranous nephropathy
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
A 24-year-old lady was evaluated for primary infertility, severe anemia and jaundice and was diagnosed to have Wilson's disease. She received d-penicillamine 1 g/day in divided doses in 2011.
In February 2013, she noticed facial puffiness, pedal edema, and frothy urine but no hematuria, oliguria, lithuria, bone pain, or bony deformities. On evaluation, she was normotensive. Her labs included proteinuria 3+, nil active sediments, sterile urine, 24 h urine protein of 10.9 g, hemoglobin of 12.2 g/dl, normal bleeding and clotting profile, serum creatinine of 0.8 mg/dl, normal liver function tests, elevated total cholesterol and triglycerides. Ultrasonography of abdomen revealed normal-sized kidneys with preserved corticomedullary differentiation. Renal biopsy under light microscopy [Figure 1] showed six glomeruli with normal cellularity, patent capillary loops, and normal mesangial cellularity. Tubulointerstitium and vessels were unremarkable. Basement membrane showed pinhole lesions on methenamine-silver stain. Immunofluorescence revealed three glomeruli with IgG 3+ and C3c 2+ in capillary walls. A diagnosis of membranous nephropathy (MN) was made.
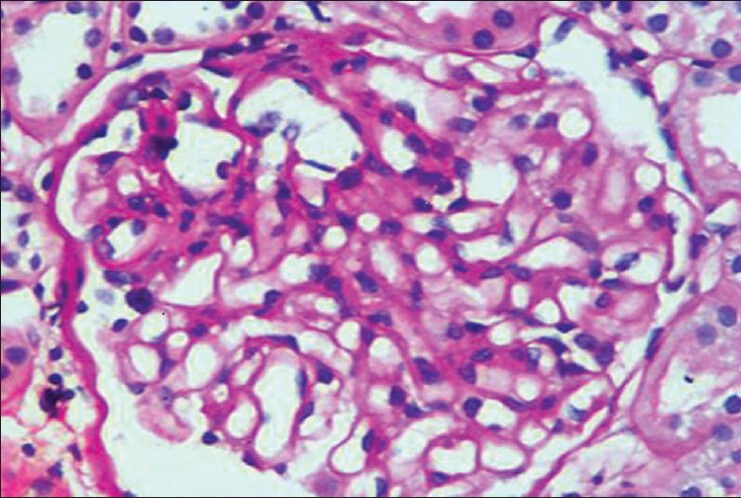
- Light microscopic picture: Normal sized glomerulus with patent capillary loops and uniform thickening of capillary wall
Serum auto-antibodies to M type Phospholipase A2 receptor (MPLA2 R), on indirect immunofluorescence was negative (1:10 dilution). The prevalence of MPLA2 R antibodies in patients with primary MN is 68.5%.[1] There is still 30% false negativity with serum MPLA2 R antibodies in primary MN. Tissue staining for MPLA2 R has sensitivity of 75% and specificity of 83%.[2] Tissue staining for MPLA2 R could not be done in our patient.
D-penicillamine was stopped and she continued oral zinc and vitamins. After 3 months of drug withdrawal, the proteinuria started improving. At 5 months, 24 h urine protein was 4.2 g. At last follow-up on 28.10.13, her 24 h urine protein was 960 mg and serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl.
Secondary MN is due to autoimmune diseases, chronic infections, malignancy, therapeutic agents, or denovo MN in renal allograft. The most common therapeutic agents implicated in secondary MN are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mercury-containing skin lightening agents, d-penicillamine, gold salts, bucillamine, antitumor necrosis factor agents, etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab. D-penicillamine-induced MN can occur at any age and usually develops within 6-12 months of exposure to the offending agent, but the onset may be delayed for 3-4 years.[3] Our patient developed MGN after 18 months of exposure to d-penicillamine. The spectrum of d-penicillamine induced nephropathy is-MN (80%), tubulointerstitial disease, minimal change disease, crescentic glomerulonephritis, Goodpasture's syndrome and renal-limited vasculitis.[4] The mean time to resolution of proteinuria was 9-12 months, and in some cases it may take up to 2-3 years. In the majority proteinuria disappeared within 7 months after stoppage of d-penicillamine. Patients treated with corticosteroids had a faster response.[5]
This letter was intended to share the availability of serum MPLA2R antibody testing and tissue staining for MPLA2 R and to reiterate that d-penicillamine induced MN is potentially reversible once it is stopped.
References
- An immunofluorescence test for phospholipase-A 2 -receptor antibodies and its clinical usefulness in patients with membranous glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:2526-32.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pathogenesis of membranous nephropathy: Recent advances and future challenges. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:203-13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Determination of primary versus secondary membranous glomerulopathy utilizing phospholipase A 2 receptor staining in renal biopsies. Mod Pathol. 2013;26:709-15.
- [Google Scholar]






