Translate this page into:
Frequency and clinicopathological correlations of histopathological variants of pediatric idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
There is no information on the frequency and clinicopathological correlations of the histopathological variants of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) in children presenting with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in Pakistan. All consecutive children (≤17 years) who presented with INS, and in whom the histological diagnosis of FSGS was made on renal biopsies, were included in this prospective study. Their clinical, laboratory, and histopathological features at the time of presentation were noted from the case files and the biopsy reports for analysis and clinicopathological correlations. Out of 138 children, 93 (67.4%) were males and 45 (32.6%) were females. The mean age was 8.95 ± 4.14 (range: 1.5-17) years. All had NS, with steroid dependant NS (SDNS) in 45 (32.6%) and steroid resistant NS (SRNS) in 93 (67.4%) cases. Renal dysfunction at the time of presentation was found in six (4.3%) children. Global glomerulosclerosis was found in 68 (49.3%) cases. The mean number of glomeruli involved by segmental scarring was 2.98 ± 2.44. FSGS, not otherwise specified (NOS) was the most prevalent variant, comprising 89.1% of all cases. Collapsing variant comprised 8%, tip variant 1.4%, perihilar 0.7%, and cellular 0.7%. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis was found in 13 (9.4%) cases. Mild interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy was found in 95 (68.6%) cases, moderate in 18 (13%), and severe in two (1.4%) cases. In conclusion, FSGS, NOS variant was the highly prevalent variant, while collapsing type was also found in small but significant number of cases. Remaining three variants were distinctly rare in our children.
Keywords
Children
focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
nephrotic syndrome
Pakistan
variants
Introduction
Primary or idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is now well-recognized as one of the predominant causes of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in both children and adults worldwide.[12345] Pediatric FSGS is a disease of increasing incidence throughout the world especially during the past two and half decades and represents a major cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Recent studies from different parts of the world suggest that the incidence of FSGS is on rise, especially among the non-white races.[67] We have earlier reported a frequency of FSGS in children of 38.14% and it was the second most common cause of INS in that study after minimal change disease (MCD) and its variants.[89]
FSGS is not a single disease, but rather a heterogeneous group of histological lesions characterized by variable amount of proteinuria, usually of nephrotic range and histologically by focal and segmental glomerular scarring and parenchymal chronic changes.[101112] Recently, an attempt has been made to categorize these heterogeneous lesions into five distinct hierarchically arranged categories, the so called Columbia classification of FSGS.[1314] The variants include FSGS, not otherwise specified (NOS), perihilar, cellular, collapsing, and tip variants.[1314] Various studies have been published elaborating the clinicopathological characteristics of these histological variants of FSGS in both children and adults.[15161718192021] We have earlier reported the frequencies and clinicopathological characteristics of these variants in adult nephrotic patients.[22] Several studies have shown that these variants have different etiologies, pathogenetic mechanisms, and diverse clinical behavior in terms of presentation, progression of disease, and long-term outcome.[15161718192021] However, there is some dispute regarding the predictive value of these variants in the pediatric population.[23] There is no study on the frequency of histological variants and clinical presentation of FSGS variants in pediatric patients from Pakistan.
The main objective of this study was to determine the frequencies and the clinicopathological correlations of the histopathological variants of FSGS in children presenting with INS at our center. Moreover, we have also compared our findings with those already reported from different parts of the world.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted from January 2009 to December 2012 at the department of Histopathology, Sindh Institute of Urology and Transplantation (SIUT). All consecutive children (≤17 years) who presented with INS at pediatric nephrology outpatient department (OPD), SIUT and in whom the histological diagnosis of FSGS was made on percutaneous ultrasound-guided native renal biopsies, were included in the analysis. The biopsies were studied by light microscopy (LM), immunoflourescence (IF), and electron microscopy (EM) as described in detail in our previous report.[12] All renal biopsies were examined by two experienced nephropathologists, first independently and then conjointly to arrive at a consensus diagnosis and classification of the lesion. FSGS was diagnosed when there was sclerosis and/collapse of capillary tufts involving part (segmental) of some but not all (focal) glomeruli. Adequacy of the renal biopsy was determined by the presence of the defining lesion on the biopsy, irrespective of the number of glomeruli. The minimum number of glomeruli per biopsy was four with a histologic diagnosis of FSGS. Cases with known etiology of segmental glomerulosclerosis, like lupus nephritis or immunoglobulin (Ig) A nephropathy (IgAN), or reflux nephropathy were excluded. When a histologic diagnosis of collapsing FSGS was made, a search was made by the nephrologists for the etiologic agents including viral and autoimmune markers. Among the viruses, serology for hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Written informed consent was taken from the patients or parents for the biopsy procedure and for inclusion in the study. Their clinical and laboratory parameters at the time of presentation were recorded from the case histories. The histological features, IF findings and final diagnosis were recorded from the original renal biopsy request forms. The standardized definitions of NS, steroid response, renal failure, and remission were used as in our previous studies.[910]
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using the IBM compatible Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) for Windows version 10 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive statistics such as mean ± standard deviation (SD) were used for continuous variables such as age and laboratory data. Numbers (%) were used to describe the proportion of categorical variables such as sex and the frequency of histological variants.
Pearson's correlation test was carried to determine the association of various clinical and pathological parameters with the morphological variants of FSGS. A P value of ≤ 0.05 was considered to be significant.
Results
The main demographic and clinical parameters of included cohort are shown in Table 1. A total of 138 children met the study inclusion criteria and were entered into the study. Of these, 93 (67.4%) were males and 45 (32.6%) were females, with a male to female ratio of 2:1. Their mean age was 8.95 ± 4.14 years with a range of 1.5-17 years.
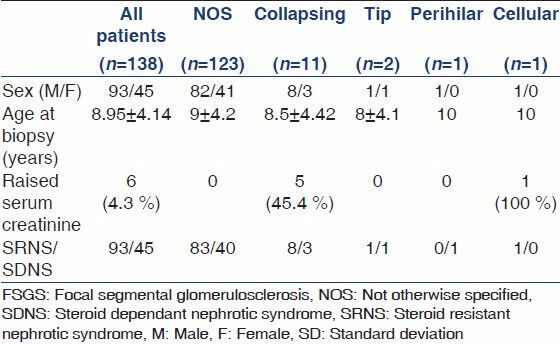
All 138 children by inclusion criteria had NS. As per biopsy indications in children at our center, steroid dependent NS (SDNS) was the reason for biopsy in 45 (32.6%) cases and steroid resistant (SRNS) in 93 (67.4%) cases. Renal dysfunction at the time of presentation was found in six (4.3%) of the children. Five of these children had collapsing FSGS on their renal biopsies and one, the cellular variant.
FSGS constituted 33.4% of all native renal biopsies done for INS in children during the study period. The principal histopathologic features on renal biopsies from 138 children are given in Table 2 and depicted in Figures 1 and 2. Our results indicate that FSGS, NOS is highly prevalent variant, comprising 89.1% of all cases. Collapsing variant comprised 8%, tip variant 1.4% perihilar 0.7%, and cellular 0.7%. The mean number of glomeruli included in all biopsies was 15.31 ± 8.17. Global glomerulosclerosis was found in 68 (49.3%) of all cases. No global glomerulosclerosis was found in 70 (50.7%) of cases. The number of globally sclerosed glomeruli ranged from 0 to 16 in an individual biopsy and the mean was 1.46 ± 2.34 per biopsy. The mean number of glomeruli involved by segmental scarring was 2.98 ± 2.44. The nonscarred areas of the glomeruli showed variable degrees of mesangial proliferation in 42% of the biopsies, while 58% showed minor changes of the non-sclerotic portions of the glomeruli. The vasculopathy was distinctly rare, given the young age of the cohort. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis was found in 13 (9.4%) cases, while no biopsy showed fibrointimal thickening (FITC) of arteries. The chronic parenchymal changes in the form of interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy (IFTA) were quite prevalent, however. Mild IFTA was found in 95 (68.6%) of cases, moderate in 18 (13%), and severe in two (1.4%) cases; while no IFTA was found in 23 (16.7%) cases. The IF examination of the biopsies showed focal to diffuse mesangial positivity of IgM in 57 (41.3%) cases associated with C3 deposition in 18 (13%) and C1q in five (3.69%) cases; while IgG and IgA were negative in all biopsies. All cases of collapsing FSGS tested negative for HCV, HBV, CMV, and HIV serology as well as autoimmune markers.


- (a) Global glomerulosclerosis. Although this lesion is not required for the diagnosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, it is frequently present in association with segmental glomerulosclerosis in advanced stages of the disease (Silver, ×200). (b) Segmental glomerulosclerosis involving more than half of the glomerulus with the scarring process associated with adhesion formation with Bowman's capsule in the FSGS, not otherwise specified (NOS) variant (Silver, ×200). (c) Tip variant of FSGS involving the tubular pole (periodic acid-Schiff, ×200). (d) The perihilar location of segmental sclerosis in a case of perihilar FSGS (PAS, ×200)

- (a) Cellular variant of FSGS (PAS, ×200). (b) Segmental collapse of capillary tufts associated with podocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy in a case of collapsing FSGS (Silver, ×200). (c) High-power view showing capillary collapse and podocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy (Silver, ×400). (d) The tubulointerstitial compartment reveals moderate interstitial inflammation, tubular atrophy, and typical hyaline casts with scalloped edges in some of the tubular lumena (Silver, ×200)
There was no significant association of the sex (P = 0.84), biopsy indications (P = 0.56), global glomerulosclerosis (P = 0.99), segmental glomerulosclerosis (P = 0.99), mesangial proliferation (P = 0.73), minor changes (P = 0.33), IFTA (P = 0.07), or vasculopathy (P = 0.98) with the histological variants. The only significant association among the clinical variables was with renal dysfunction at presentation, which was found in six cases (P = 0.001). Five of these patients belonged to collapsing variant and one to the cellular variant. In three of these patients with collapsing FSGS, serum creatinine increased slightly from 1.5, 3.2, and 2.4 mg/dl to 1.8, 4.5, and 2.8 mg/dl at 2, 12, and 18 months of follow-up, respectively. In one patient with collapsing FSGS, creatinine improved slightly from 1.8 to 1.5 mg at 5 months follow-up. Two children, one with collapsing and one with cellular variants, with renal dysfunction at presentation, were soon lost to follow-up. Global glomerulosclerosis and IFTA also correlated with renal failure at presentation (P-values: 0.007 and 0.001, respectively). Among the IF results, no significant association was seen with IgM (P = 0.054), while both C3 and C1q showed significant correlations with the histological variants being found more commonly in NOS variants (P = 0.001 and 0.001, respectively). It should be noted that some of the correlations may not reflect the true picture because of the extremely small number of cases.
EM findings in a representative case of FSGS, NOS, are given in Figure 3. Ultrastructural study was basically useful in excluding the secondary causes of FSGS.

- (a) Electron micrograph showing extensive fusion of foot processes and marked cytoplasmic vacuolization of podocytes (electron microscopy, ×3,000). (b) Electron micrograph showing extensive fusion of foot processes, irregular thickening, and wrinkling of glomerular basement membrane (EM, ×10,000)
Table 3 provides a comparison of the prevalence of different histological variants of FSGS in studies from Brazil, Korea, Egypt, and USA. As is evident from this table, FSGS, NOS is the predominant type all over the world. However, the relative frequencies of this and other variants vary markedly among the studies.

Discussion
This analysis is a timely contribution to the literature on the histological variants of FSGS in pediatric patients presenting with INS from this part of the world. To our knowledge, this is the largest study on the pathological variants of pediatric FSGS in literature and we are of the view that this study provides important insights into the presenting clinicopathological features and prevalence of the different variants of FSGS in the pediatric population from Pakistan.
The last two and half decades have witnessed a rising trend in the incidence of FSGS in both children and adults.[234567] Part of this rise is attributed to real increase in the incidence of the condition and part to a heightened awareness and recognition of the lesion among the nephropathological community. One of the main reasons for the heightened interest in the lesion is the aggressive nature of the condition.[9] FSGS constituted 33.4% of all renal biopsies done for INS in children in the current study. This is more or less similar to that observed in our earlier study carried out from 1996 to 2008.[8] This shows that the prevalence of FSGS during the last 17 years has remained relatively static. We however did not specifically analyze the trend in the incidence of the different histological variants of FSGS in this study. Approximately 30-40% of adult patients with FSGS develop end-stage renal disease (ESRD) over 10 years of follow-up. The prognosis is relatively more favorable in children, but the data in literature showed conflicting results.[51923]
The increasing recognition and reporting of detailed pathological analysis of FSGS has also resulted in the subclassification of the lesion into five histological variants.[1314] The prognostic and predictive value is highly debated in both adults and children.[171823] Two earlier studies in adult patients did not find predictive value of the histological variants for the clinical outcome.[317] However, one recent study showed a poor outcome of adults with collapsing FSGS.[18]
The data in pediatric patients is scanty and the results more controversial.[23] More recent studies have found a favorable prognosis among children with primary FSGS.[1920] The improved short-term outcome in these studies may be due to earlier diagnosis and the availability of more and better therapeutic options.[23]
There are very few studies on the frequency and the clinicopathological correlations of histological variants of FSGS in children. The only available study specifically addressing this subject found only three of the five variants and included 41 children.[23] A few other studies have addressed individual variants of primary FSGS, such as collapsing FSGS.[24] As compared with the study by Silverstein et al.,[23] we were able to demonstrate all the five variants of FSGS in our cohort, which is also comparatively larger in size as compared with the aforementioned study. However, the prevalence of some of these histological variants of FSGS was very low. Moreover, the frequency distribution of the variants also differed markedly in these two studies. Similar to our study, Paik et al.,[20] from Korea also found all the five variants of FSGS in their cohort and the frequency distribution is also somewhat similar to that of ours. El-Refaey et al.,[21] from Egypt were also able to find somewhat similar results to our study. FSGS, NOS was vastly predominant in our cohort, while cellular and perihilar variants were distinctly rare. FSGS, NOS is the predominant variant in most of the reported studies in both children and adults. One important observation is the prevalence of collapsing FSGS in a small but significant number of our children. Although, this variant is not as frequent as observed in the study by Silverstein et al.,[23] it is, nonetheless, not very uncommon. It is important to recognize this lesion accurately, as it carries a guarded prognosis among all the variants. We did not find a cause for this lesion as for all cases of FSGS included in the study, especially the viral and autoimmune diseases. Renal dysfunction at presentation was significantly associated with the histological variants of FSGS. In majority of children with collapsing FSGS, renal failure progressed over variable period of follow-up. Only one of the collapsing FSGS children showed marginal improvement in renal function over 6 months of follow-up. It shows that renal dysfunction is irreversible in most of the cases with collapsing FSGS.
The frequency distribution of the histological variants of FSGS in our pediatric cohort was compared with Brazilian, Korean, Egyptian, and multiethnic North American cohorts.[19202123] It is obvious from these comparisons that FSGS, NOS is the predominant variant among all studies; however, the frequency varies widely. Our frequency more closely resembles the Brazilian and Egyptian studies than North American or Korean figures. These differences in the frequencies may reflect different biopsy indications, sample size and other environmental and genetic factors.[19202123]
There are certain limitations in this study, such as its origin from a single center, more restrictive biopsy indications, and a cross-sectional nature of the study with no information on the treatment, clinical outcome, renal survival, and the follow-up.
In conclusion, our results show that FSGS, NOS is the highly prevalent variant among nephrotic children in Pakistan. Collapsing variant is found in a small but significant number of children, while the other three variants are distinctly rare. Future long-term follow-up studies are needed to determine the impact of these variants on renal survival and clinical outcome.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge with gratitude the help and efforts of Dr. Syed Wajahat Ali Rizvi, EM consultant, and Perveen Akhter, EM technologist, in obtaining the EM data and photographs.
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- Trends in the epidemiology of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Semin Nephrol. 2003;23:172-82.
- [Google Scholar]
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. A report of the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. Kidney Int. 1985;27:442-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- High incidence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999;13:13-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Age and ethnicity affect the risk and outcome of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 1998;12:764-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Changing characteristics of childhood nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2005;68:1275-81.
- [Google Scholar]
- Changing patterns in the histopathology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Kidney Int. 1999;55:1885-90.
- [Google Scholar]
- Histopathological spectrum of childhood nephrotic syndrome in Pakistan. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2009;13:589-93.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment and prognosis of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children from Pakistan. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant. 2012;23:513-20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Histological heterogeneity of glomerular segmental lesions in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012;44:183-96.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Sem Nephrol. 2003;23:117-34.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: A working proposal. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:368-82.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinicopathologic study of different variants of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2007;36:11-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Study of the morphologic variants of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: A Brazilian report. J Bras Pathol Med Lab. 2012;48:211-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults: Prognostic value of histologic variants. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;25:845-52.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and pathologic characteristics of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis pathologic variants. Kidney Int. 2006;69:920-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinical course of 110 children and adolescents with primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:482-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children: Clinical course and prognosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:389-95.
- [Google Scholar]
- Primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in Egyptian children: A 10-year single-centre experience. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25:1369-73.
- [Google Scholar]
- Frequency and clinicopathological characteristics of variants of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults presenting with nephrotic syndrome. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:28-35.
- [Google Scholar]
- Presenting features and short-term outcome according to pathologic variant in childhood primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:700-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Idiopathic collapsing glomerulopathy in children. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008;12:348-53.
- [Google Scholar]







